中断处理 - 上半部(硬中断) 由于 APIC中断控制器 有点小复杂,所以本文主要通过 8259A中断控制器 来介绍Linux对中断的处理过程。
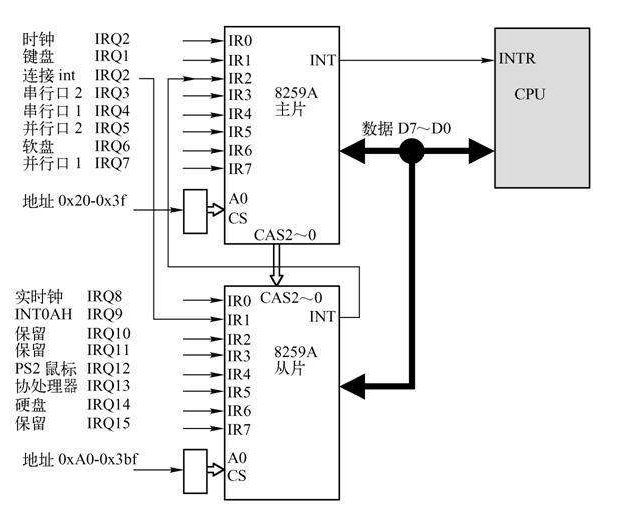
中断处理相关结构 前面说过,8259A中断控制器 由两片 8259A 风格的外部芯片以 级联 的方式连接在一起,每个芯片可处理多达 8 个不同的 IRQ(中断请求),所以可用 IRQ 线的个数达到 15 个。如下图:
在内核中每条IRQ线由结构体 irq_desc_t 来描述,irq_desc_t 定义如下:
typedef struct {unsigned int status; struct irqaction *action ;unsigned int depth; spinlock_t lock;irq_desc_t ;
下面介绍一下 irq_desc_t 结构各个字段的作用:
status: IRQ线的状态。handler: 类型为 hw_interrupt_type 结构,表示IRQ线对应的硬件相关处理函数,比如 8259A中断控制器 接收到一个中断信号时,需要发送一个确认信号才会继续接收中断信号的,发送确认信号的函数就是 hw_interrupt_type 中的 ack 函数。action: 类型为 irqaction 结构,中断信号的处理入口。由于一条IRQ线可以被多个硬件共享,所以 action 是一个链表,每个 action 代表一个硬件的中断处理入口。depth: 防止多次开启和关闭IRQ线。lock: 防止多核CPU同时对IRQ进行操作的自旋锁。
hw_interrupt_type 这个结构与硬件相关,这里就不作介绍了,我们来看看 irqaction 这个结构:
struct irqaction {void (*handler)(int , void *, struct pt_regs *);unsigned long flags;unsigned long mask;const char *name;void *dev_id;struct irqaction *next ;
下面说说 irqaction 结构各个字段的作用:
handler: 中断处理的入口函数,handler 的第一个参数是中断号,第二个参数是设备对应的ID,第三个参数是中断发生时由内核保存的各个寄存器的值。flags: 标志位,用于表示 irqaction 的一些行为,例如是否能够与其他硬件共享IRQ线。name: 用于保存中断处理的名字。dev_id: 设备ID。next: 每个硬件的中断处理入口对应一个 irqaction 结构,由于多个硬件可以共享同一条IRQ线,所以这里通过 next 字段来连接不同的硬件中断处理入口。
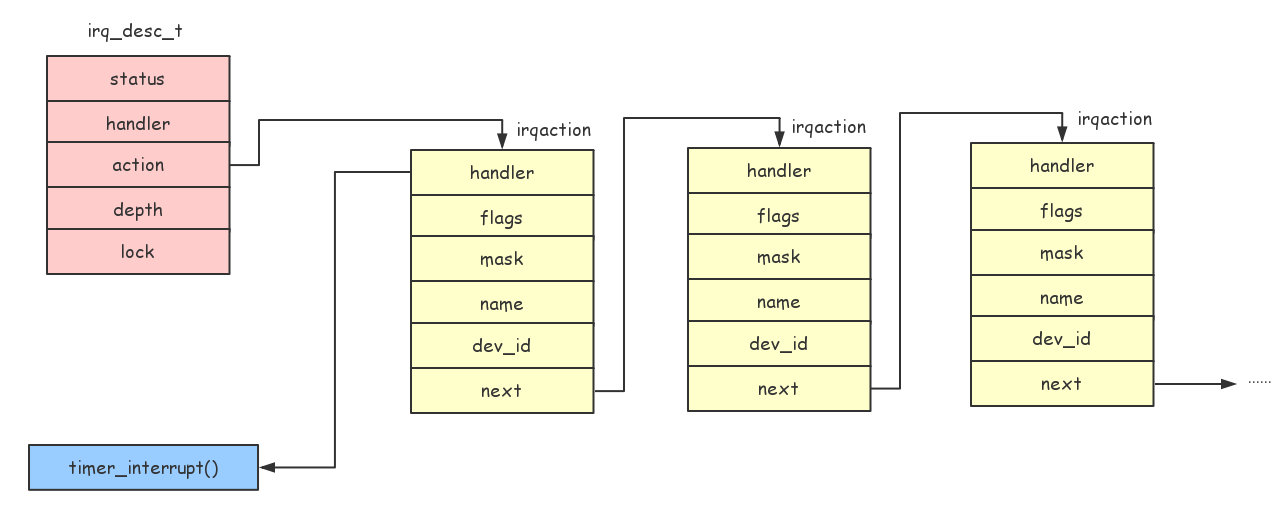
irq_desc_t 结构关系如下图:
注册中断处理入口 在内核中,可以通过 setup_irq() 函数来注册一个中断处理入口。setup_irq() 函数代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 int setup_irq (unsigned int irq, struct irqaction * new ) int shared = 0 ;unsigned long flags;struct irqaction *old , **p ;irq_desc_t *desc = irq_desc + irq;if ((old = *p) != NULL ) {if (!(old->flags & new ->flags & SA_SHIRQ)) {return -EBUSY;do {while (old);1 ;new ;if (!shared) {0 ;return 0 ;
setup_irq() 函数比较简单,就是通过 irq 号来查找对应的 irq_desc_t 结构,并把新的 irqaction 连接到 irq_desc_t 结构的 action 链表中。要注意的是,如果设备不支持共享IRQ线(也即是 flags 字段没有设置 SA_SHIRQ 标志),那么就返回 EBUSY 错误。
我们看看 时钟中断处理入口 的注册实例:
static struct irqaction irq0 = {0 , "timer" , NULL , NULL };void __init time_init (void ) 0 , &irq0);
可以看到,时钟中断处理入口的IRQ号为0,处理函数为 timer_interrupt(),并且不支持共享IRQ线(flags 字段没有设置 SA_SHIRQ 标志)。
处理中断请求 当一个中断发生时,中断控制层会发送信号给CPU,CPU收到信号会中断当前的执行,转而执行中断处理过程。中断处理过程首先会保存寄存器的值到栈中,然后调用 do_IRQ() 函数进行进一步的处理,do_IRQ() 函数代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 asmlinkage unsigned int do_IRQ (struct pt_regs regs) int irq = regs.orig_eax & 0xff ; int cpu = smp_processor_id();irq_desc_t *desc = irq_desc + irq;struct irqaction * action ;unsigned int status;NULL ;if (!(status & (IRQ_DISABLED | IRQ_INPROGRESS))) { if (!action) goto out;for (;;) {if (!(desc->status & IRQ_PENDING)) break ;end (irq);if (softirq_active(cpu) & softirq_mask(cpu))return 1 ;
do_IRQ() 函数首先通过IRQ号获取到其对应的 irq_desc_t 结构,注意的是同一个中断有可能发生多次,所以要判断当前IRQ是否正在被处理当中(判断 irq_desc_t 结构的 status 字段是否设置了 IRQ_INPROGRESS 标志),如果不是处理当前,那么就获取到 action 链表,然后通过调用 handle_IRQ_event() 函数来执行 action 链表中的中断处理函数。
如果在处理中断的过程中又发生了相同的中断(irq_desc_t 结构的 status 字段被设置了 IRQ_INPROGRESS 标志),那么就继续对中断进行处理。处理完中断后,调用 do_softirq() 函数来对中断下半部进行处理(下面会说)。
接下来看看 handle_IRQ_event() 函数的实现:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 int handle_IRQ_event (unsigned int irq, struct pt_regs * regs, struct irqaction * action) int status;int cpu = smp_processor_id();1 ; if (!(action->flags & SA_INTERRUPT)) do {while (action);if (status & SA_SAMPLE_RANDOM)return status;
handle_IRQ_event() 函数非常简单,就是遍历 action 链表并且执行其中的处理函数,比如对于 时钟中断 就是调用 timer_interrupt() 函数。这里要注意的是,如果中断处理过程能够开启中断的,那么就把中断打开(因为CPU接收到中断信号时会关闭中断)。
中断处理 - 下半部(软中断) 由于中断处理一般在关闭中断的情况下执行,所以中断处理不能太耗时,否则后续发生的中断就不能实时地被处理。鉴于这个原因,Linux把中断处理分为两个部分,上半部 和 下半部,上半部 在前面已经介绍过,接下来就介绍一下 下半部 的执行。
一般中断 上半部 只会做一些最基础的操作(比如从网卡中复制数据到缓存中),然后对要执行的中断 下半部 进行标识,标识完调用 do_softirq() 函数进行处理。
softirq机制 中断下半部 由 softirq(软中断) 机制来实现的,在Linux内核中,有一个名为 softirq_vec 的数组,如下:
static struct softirq_action softirq_vec [32];
其类型为 softirq_action 结构,定义如下:
struct softirq_action { void (*action)(struct softirq_action *);void *data;
softirq_vec 数组是 softirq 机制的核心,softirq_vec 数组每个元素代表一种软中断。但在Linux中只定义了四种软中断,如下:
enum 0 ,
HI_SOFTIRQ 是高优先级tasklet,而 TASKLET_SOFTIRQ 是普通tasklet,tasklet是基于softirq机制的一种任务队列(下面会介绍)。NET_TX_SOFTIRQ 和 NET_RX_SOFTIRQ 特定用于网络子模块的软中断(不作介绍)。
注册softirq处理函数 要注册一个softirq处理函数,可以通过 open_softirq() 函数来进行,代码如下:
void open_softirq (int nr, void (*action)(struct softirq_action*), void *data) unsigned long flags;int i;for (i=0 ; i<NR_CPUS; i++)1 <<nr);
open_softirq() 函数的主要工作就是向 softirq_vec 数组添加一个softirq处理函数。
Linux在系统初始化时注册了两种softirq处理函数,分别为 TASKLET_SOFTIRQ 和 HI_SOFTIRQ:
void __init softirq_init () NULL );NULL );
处理softirq 处理softirq是通过 do_softirq() 函数实现,代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 asmlinkage void do_softirq () int cpu = smp_processor_id();if (in_interrupt())return ;if (active) {struct softirq_action *h ;do {if (active & 1 )1 ;while (active);if ((active &= mask) != 0 )goto retry;return ;goto restart;
前面说了 softirq_vec 数组有32个元素,每个元素对应一种类型的softirq,那么Linux怎么知道哪种softirq需要被执行呢?在Linux中,每个CPU都有一个类型为 irq_cpustat_t 结构的变量,irq_cpustat_t 结构定义如下:
typedef struct {unsigned int __softirq_active;unsigned int __softirq_mask;irq_cpustat_t ;
其中 __softirq_active 字段表示有哪种softirq触发了(int类型有32个位,每一个位代表一种softirq),而 __softirq_mask 字段表示哪种softirq被屏蔽了。Linux通过 __softirq_active 这个字段得知哪种softirq需要执行(只需要把对应位设置为1)。
所以,do_softirq() 函数首先通过 softirq_mask(cpu) 来获取当前CPU对应被屏蔽的softirq,而 softirq_active(cpu) & mask 就是获取需要执行的softirq,然后就通过对比 __softirq_active 字段的各个位来判断是否要执行该类型的softirq。
tasklet机制 前面说了,tasklet机制是基于softirq机制的,tasklet机制其实就是一个任务队列,然后通过softirq执行。在Linux内核中有两种tasklet,一种是高优先级tasklet,一种是普通tasklet。这两种tasklet的实现基本一致,唯一不同的就是执行的优先级,高优先级tasklet会先于普通tasklet执行。
tasklet本质是一个队列,通过结构体 tasklet_head 存储,并且每个CPU有一个这样的队列,我们来看看结构体 tasklet_head 的定义:
struct tasklet_head { struct tasklet_struct *list ;struct tasklet_struct { struct tasklet_struct *next ;unsigned long state;atomic_t count;void (*func)(unsigned long );unsigned long data;
从 tasklet_head 的定义可以知道,tasklet_head 结构是 tasklet_struct 结构队列的头部,而 tasklet_struct 结构的 func 字段正式任务要执行的函数指针。Linux定义了两种的tasklet队列,分别为 tasklet_vec 和 tasklet_hi_vec,定义如下:
struct tasklet_head tasklet_vec [NR_CPUS ];struct tasklet_head tasklet_hi_vec [NR_CPUS ];
可以看出,tasklet_vec 和 tasklet_hi_vec 都是数组,数组的元素个数为CPU的核心数,也就是每个CPU核心都有一个高优先级tasklet队列和一个普通tasklet队列。
调度tasklet 如果我们有一个tasklet需要执行,那么高优先级tasklet可以通过 tasklet_hi_schedule() 函数调度,而普通tasklet可以通过 tasklet_schedule() 调度。这两个函数基本一样,所以我们只分析其中一个:
static inline void tasklet_hi_schedule (struct tasklet_struct *t) if (!test_and_set_bit(TASKLET_STATE_SCHED, &t->state)) {int cpu = smp_processor_id();unsigned long flags;list ;list = t;
函数参数的类型是 tasklet_struct 结构的指针,表示需要执行的tasklet结构。tasklet_hi_schedule() 函数首先判断这个tasklet是否已经被添加到队列中,如果不是就添加到 tasklet_hi_vec 队列中,并且通过调用 __cpu_raise_softirq(cpu, HI_SOFTIRQ) 来告诉softirq需要执行 HI_SOFTIRQ 类型的softirq,我们来看看 __cpu_raise_softirq() 函数的实现:
static inline void __cpu_raise_softirq(int cpu, int nr)1 <<nr);
可以看出,__cpu_raise_softirq() 函数就是把 irq_cpustat_t 结构的 __softirq_active 字段的 nr位 设置为1。对于 tasklet_hi_schedule() 函数就是把 HI_SOFTIRQ 位(0位)设置为1。
前面我们也介绍过,Linux在初始化时会注册两种softirq,TASKLET_SOFTIRQ 和 HI_SOFTIRQ:
void __init softirq_init () NULL );NULL );
所以当把 irq_cpustat_t 结构的 __softirq_active 字段的 HI_SOFTIRQ 位(0位)设置为1时,softirq机制就会执行 tasklet_hi_action() 函数,我们来看看 tasklet_hi_action() 函数的实现:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 static void tasklet_hi_action (struct softirq_action *a) int cpu = smp_processor_id();struct tasklet_struct *list ;list = tasklet_hi_vec[cpu].list ;list = NULL ;while (list != NULL ) {struct tasklet_struct *t = list ;list = list ->next;if (tasklet_trylock(t)) {if (atomic_read(&t->count) == 0 ) {continue ;
tasklet_hi_action() 函数非常简单,就是遍历 tasklet_hi_vec 队列并且执行其中tasklet的处理函数。